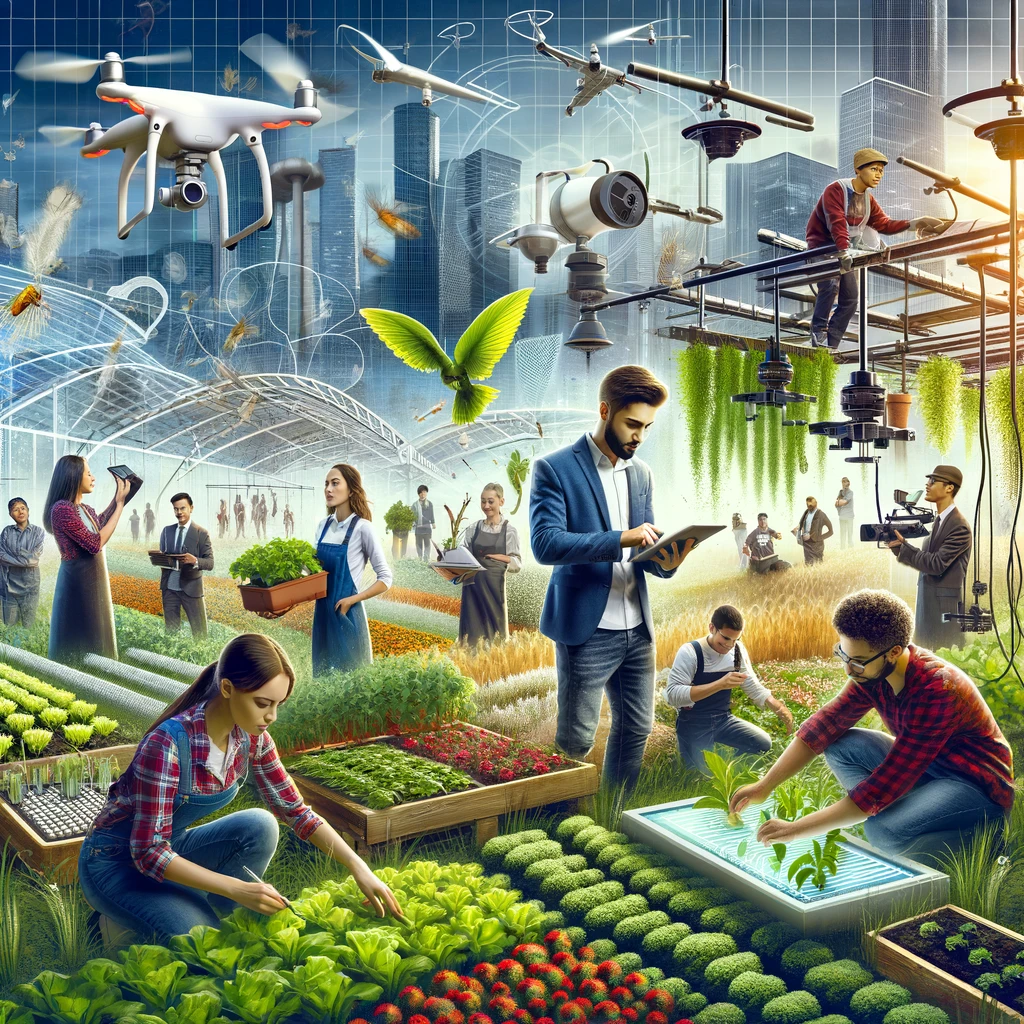
Introduction
As the agricultural sector grows, understanding the diverse career paths in agriculture is more crucial than ever. This part of our series delves into the specializations and educational pathways that can lead to a rewarding agricultural career. Building a career in agriculture offers a multitude of pathways ranging from scientific research to hands-on farming techniques. As we move to Part 2 of our blog series, we’ll focus on the specializations within agriculture, outline the educational path right from high school, and provide a detailed overview of the best agriculture universities and colleges along with their entrance exams and tuition fees. To understand if your passion really is in the Agriculture Career
Choosing the Right Path in High School
For students interested in pursuing a career paths in agriculture, selecting the appropriate subjects in the 11th and 12th grades is crucial. Here’s what you need to focus on:
Biology: Essential for understanding plant and animal biology.
Chemistry: Important for soil science and agricultural chemical applications.
Environmental Science: Offers insights into ecological aspects affecting agriculture.
Mathematics: Useful for data analysis and economic aspects of farming.
Career Paths in Agriculture Specializations
Agriculture offers a wide range of specializations, encompassing both traditional practices and new-age careers focused on sustainability and modern technologies. Here’s a comprehensive list:
Traditional Agriculture Specializations
1. Agronomy: The science of soil management and crop production.
2. Horticulture: Involves the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants.
3. Animal Science: Focuses on the breeding, genetics, and nutrition of farm animals.
4. Soil Science: Studies soil properties, classification, and management.
5. Plant Breeding: The science of enhancing plant properties for better yield and resistance.
6. Agricultural Economics: Focuses on the economic aspects and policies affecting agriculture.
7. Poultry Science: Specializes in the breeding and care of birds such as chickens and turkeys.
8. Dairy Science: Involves the production and processing of dairy products.
9. Agricultural Engineering: Applies engineering principles to agriculture, such as machinery, structures, and irrigation.
10. Entomology: The study of insects, particularly those that affect agriculture.
11. Plant Pathology: Studies plant diseases and their management.
12. Agricultural Extension: The application of scientific research and new knowledge to agricultural practices through farmer education.
13. Aquaculture: The breeding, raising, and harvesting of plants and animals in all types of water environments.
New Age and Sustainability-Focused Careers
1. Precision Agriculture: Uses GPS, IoT, and other technologies to enhance crop production efficiency and sustainability.
2. Organic Agriculture: Focuses on sustainable farming practices that do not use synthetic pesticides or fertilizers.
3. Urban Agriculture: Involves growing food in densely populated areas to reduce food miles and promote food security.
4. Agroforestry: Integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes to enhance productivity and sustainability.
5. Hydroponics and Aquaponics: Soil-less growing systems that use nutrient-rich water, which can be highly efficient and reduce land use.
6. Sustainable Agricultural Systems: Studies ways to sustainably intensify agriculture to meet global food demands.
7. Climate Smart Agriculture: Aims to increase agricultural resilience to climate change.
8. Food Security and Nutrition: Focuses on ensuring that all people have access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food.
9. Agricultural Biotechnology : Utilizes cellular and biomolecular processes to develop technologies and products to help improve agricultural practices.
10. Renewable Energy in Agriculture: Explores the use of renewable energy sources, like solar or wind power, within agricultural systems.
11. Permaculture: A philosophy of working with, rather than against, nature; it includes a set of design principles for sustainable and regenerative agriculture.
These specializations reflect the dynamic nature of agriculture, catering to both traditional agricultural practices and modern, sustainable approaches that address current global challenges. Whether you’re interested in direct farming activities, research, or policy-making, there’s likely a field in agriculture that matches your interests and skills. Check out our Part 3 – Universities and Colleges to choose for your Career paths in Agriculture. To consider your career path and its opportunities consult with us Book an appointment with our Certified Career Counselor and Coach